Best Practices for Payment Gateway Security
In the rapidly growing world of digital payments, securing transactions is critical for businesses, especially those in high-risk industries. Payment gateways, as a core component of this ecosystem, must follow best practices to ensure that customer data remains safe. Among these best practices, tokenization stands out as one of the most effective methods. Here, we will provide an overview of payment gateway security, focusing on tokenization and other essential best practices.
What is Tokenization?
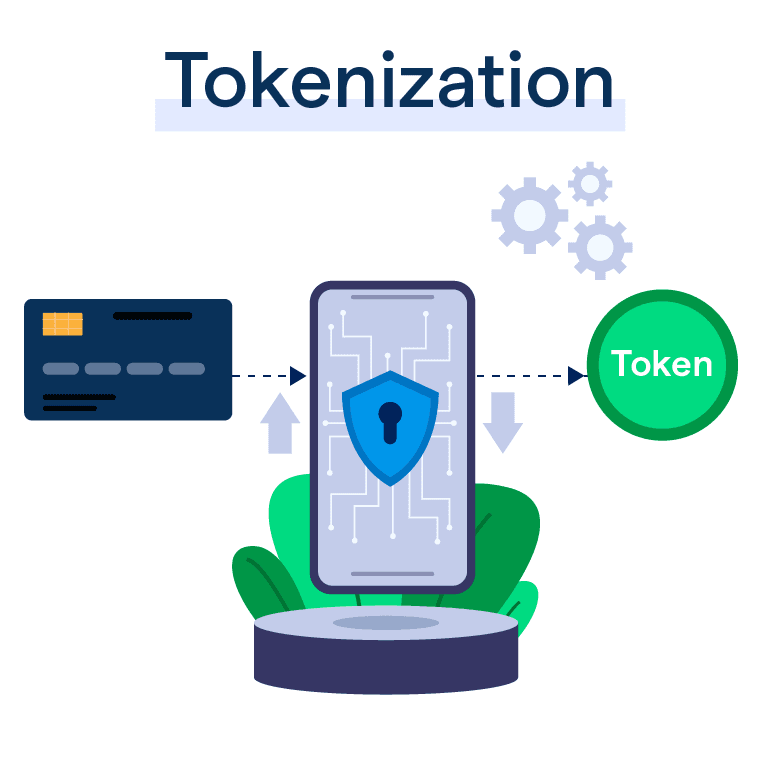
Tokenization is a security process that replaces sensitive card data with a unique identifier known as a token. Instead of storing the cardholder’s credit card number, a payment gateway can store a token that can only be used by authorized parties. This means that if a token is intercepted by a hacker, it is useless without the decryption key and cannot be traced back to the original card information.
Here’s how tokenization works in practice:
- A customer initiates a transaction and enters their payment details.
- The payment gateway encrypts the sensitive data and sends it to a secure tokenization server.
- The server generates a token that maps to the original data but has no meaningful value if compromised.
- The token is then returned to the gateway for processing, while the sensitive card data is securely stored in the tokenization vault.
By using tokens, businesses can reduce the risk of fraud, simplify PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) compliance, and protect customers from potential breaches.
Benefits of Tokenization
- Reduced Risk of Data Breaches: Since actual credit card data is not stored or transmitted during the transaction process, the likelihood of a successful breach is greatly reduced.
- PCI DSS Compliance: Tokenization simplifies the burden of PCI compliance since the actual payment data is not stored in the company’s systems.
- Fraud Prevention: Tokens cannot be reverse-engineered back to the original payment data, making them ineffective if intercepted by cybercriminals.
- Seamless Customer Experience: Tokens can be used across various platforms (e.g., in-store, online, mobile apps) without needing to re-enter payment details, enhancing the user experience.
- Improves throughput: Rebills and one-clicks have a higher chance of authorization when the transaction is attempted against a token.
Gateway Best Practices for Merchants
While tokenization is a critical component of payment security, there are several other best practices that merchants should implement to ensure robust protection:
- End-to-End Encryption (E2EE)
Encryption ensures that sensitive data is unreadable while in transit. By using end-to-end encryption, payment data is encrypted at the point of entry (e.g., when a customer enters their card information) and remains encrypted until it reaches the secure processing environment. This makes it impossible for hackers to intercept and read the data during transmission.
- Secure Socket Layer (SSL) Certificates
SSL certificates establish a secure connection between the payment gateway and the customer’s browser, encrypting the data exchanged during the transaction. Merchants should always implement SSL protocols to safeguard against man-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks.
- 3D Secure Authentication
3D Secure adds an additional layer of security by requiring customers to authenticate their identity via a one-time password (OTP) or biometric data during a transaction. This helps reduce fraud from the unauthorized use of stolen card details.
- Fraud Detection and Monitoring
Merchants should implement real-time fraud detection systems that analyze transactions for unusual patterns. Using artificial intelligence (AI), businesses can identify suspicious activities, such as multiple failed transaction attempts or purchases from high-risk locations.
- Regular Security Audits and Vulnerability Assessments
Continuous security assessments are essential to stay ahead of emerging threats. As best practice, merchants should schedule regular penetration testing, vulnerability scans, and security audits to identify and address weaknesses in the payment gateway infrastructure.
- Compliance with Regulatory Standards
Whichever gateway a merchant uses must adhere to industry regulations, such as PCI DSS, GDPR, and regional data protection laws. Compliance ensures that businesses are implementing the necessary controls to safeguard sensitive data.
As digital payments continue to evolve, securing payment data should remain a top priority for all businesses and even more important for high-risk merchants. Tokenization, along with other security practices like encryption, 3D Secure, and fraud monitoring, are essential to reducing the risk of breaches and ensuring that customer trust is maintained. By following these best practices, businesses can protect both themselves and their customers from the ever-growing threat of payment fraud.
As always, MobiusPay is here to help you navigate through your payment processing journey. Give us a call anytime!
Return to Blog







* Created by
